Automation equipment is an integral part of modern industrial operations. It refers to a wide range of machinery and devices that are designed to perform specific tasks with minimal or no human intervention. With the advent of electricity and the development of new technologies, the use of automation equipment has expanded rapidly. Today, automation equipment is used in a wide range of industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, logistics and warehousing, construction, and energy. Read More…
A recognized leader in automated assembly products. Stay competitive with Dixon's robotic screwdrivers, auto-fed screw & nut drivers, auto-fed part placers, parts feeding systems & assembly cells, including robotic assembly & vision. Every Dixon product is manufactured to assure accuracy & dependability for repetitive assembly. Dixon supports Machine Integrators with assembly products & stations. ...
Invio Automation is a leading comprehensive AGV, AMR, and robotics integrator with 10 engineering and support sites throughout North America. We specialize in heavyweight and assembly line applications.

Advent design has been in business for over 35 years providing custom automation solutions, engineering, integration solutions and machine safety services. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and see how we can help you achieve your goals.
Since 1982, Isotech has been a leader in the automation equipment industry. You can trust the accuracy of our solutions. Our experts at Isotech are always available to assist you with your needs. Feel free to contact us today to learn more information!

We have an extensive selection of products to pick from and we are confident we can find the perfect solution for your application. Our world-class items are proven for reliability and longevity. You can count on us to supply you with the best.

Del-Tron Precision is your one-stop shop for ball & crossed roller slides, multi-axis positioning and motor-ready lead screw stages, air actuators, recirculating slide guides and crossed roller rail sets. Custom linear slides are available.
More Assembly Machinery Manufacturers
Types of Automation Equipment
Automation equipment comes in various forms, each designed to perform specific tasks.
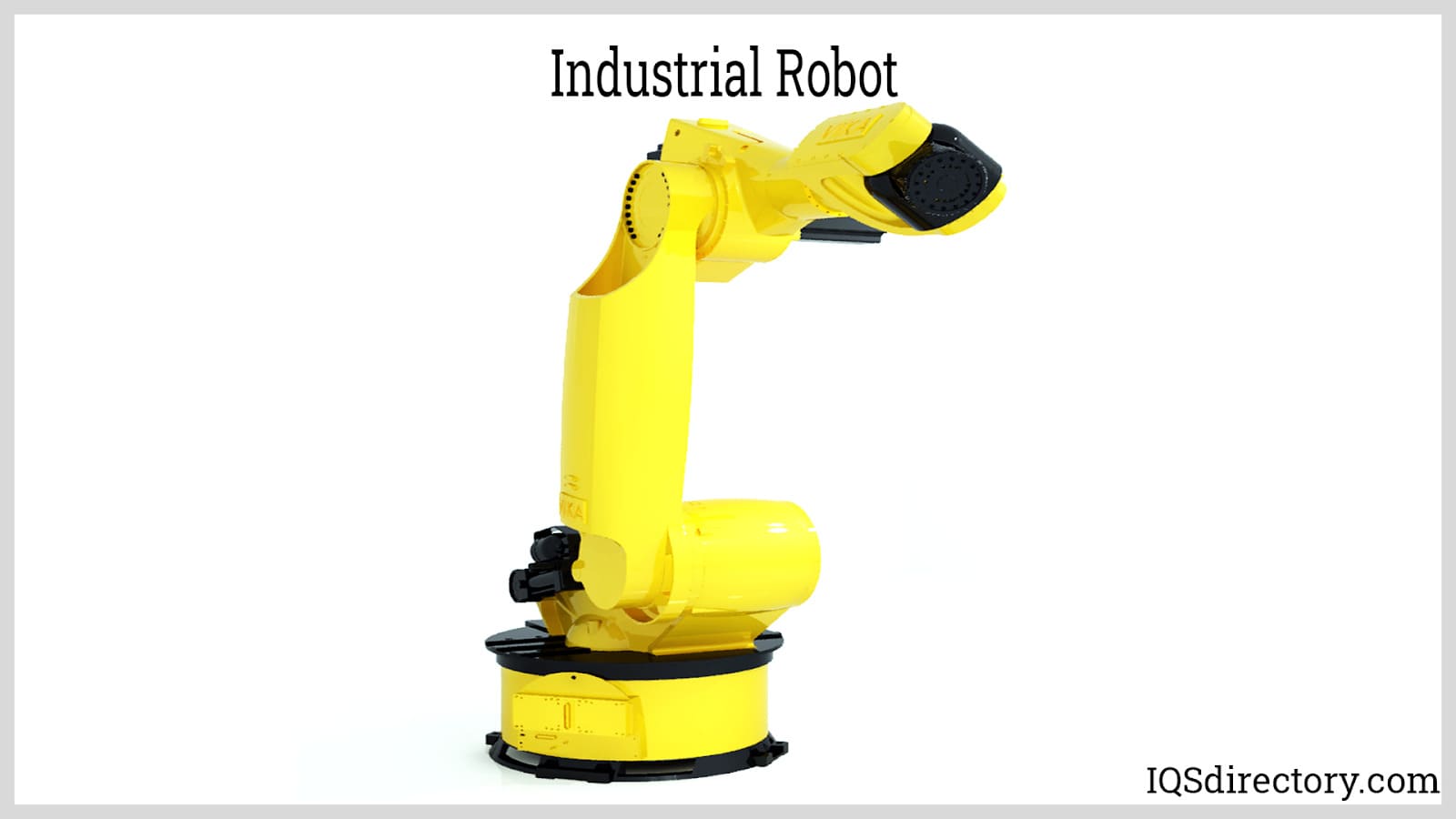
Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are highly versatile machines engineered for precise and repetitive tasks. They’re ubiquitous in manufacturing environments, handling a range of activities from assembly and welding to painting, material handling, and packaging. Depending on the specific application, these robots can be either stationary or mobile, offering flexibility and efficiency in various industrial processes.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are integral digital computing systems utilized for controlling and automating manufacturing processes. These systems gather input data from various sensors and devices, process this information through pre-defined logical algorithms, and subsequently generate output signals to manage machinery and equipment. Their application is widespread across assembly lines, conveyor systems, and various industrial machinery, where they ensure efficient, reliable, and precise operations.
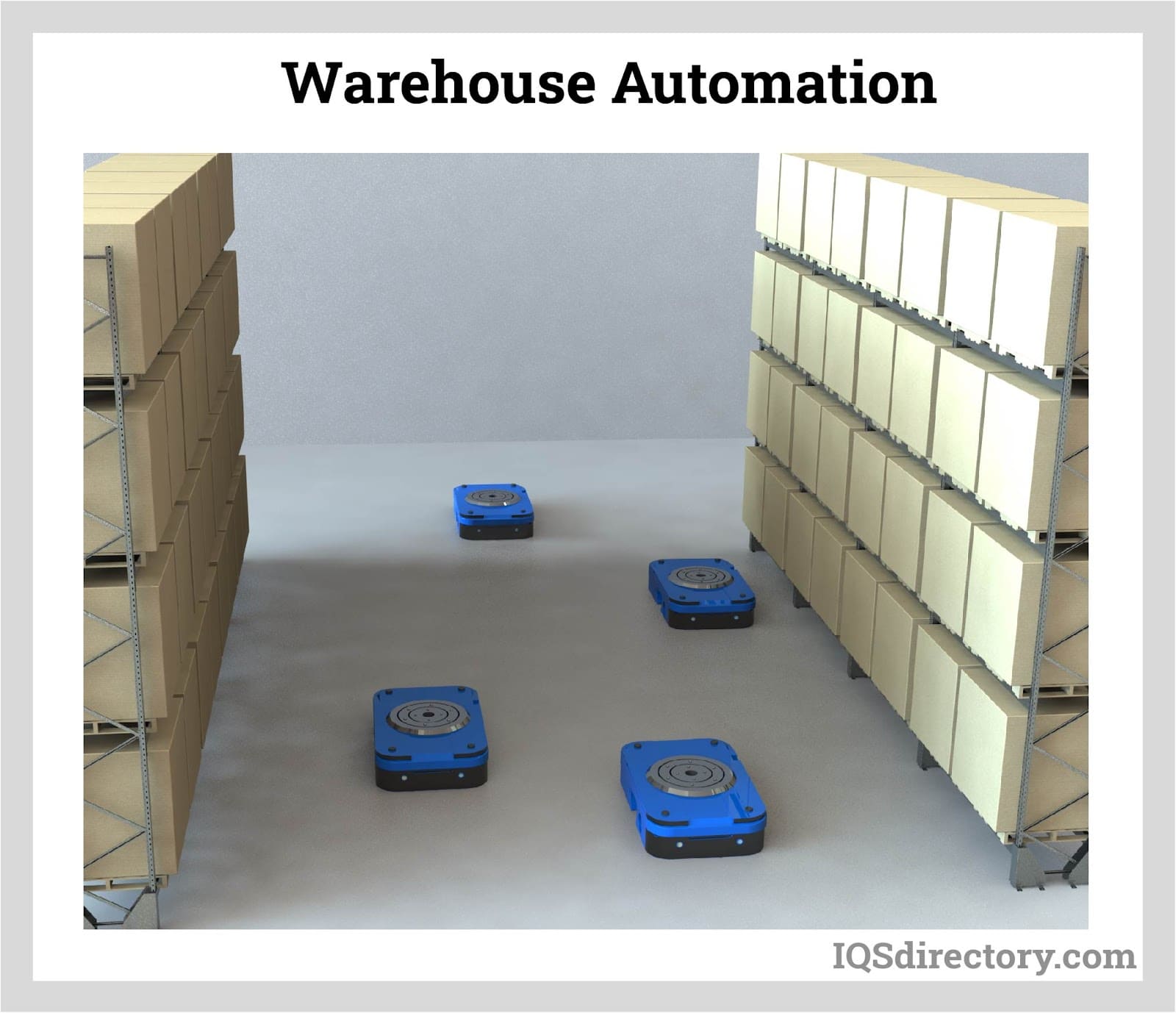
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are self-propelled units equipped with advanced sensors and navigation systems, enabling them to autonomously transport materials or goods in a facility. Widely utilized in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing plants, AGVs handle tasks such as goods transportation, order picking, and inventory management with high efficiency and precision, significantly reducing the need for human intervention in these processes.
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as 3D printing, involves creating three-dimensional objects through the successive deposition of material layers. This technology facilitates the production of intricate and customized components directly from digital models, offering significant flexibility and precision. 3D printers are extensively utilized across diverse industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace. Their applications range from rapid prototyping and product development to small-scale production, enabling efficient and cost-effective creation of complex parts that meet specific industry requirements.
Drones
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are aircraft that can be remotely piloted or autonomously operated. Equipped with advanced cameras, sensors, and other data-capturing devices, drones are revolutionizing various industries. In agriculture, they facilitate precise crop monitoring and spraying. In construction, they are invaluable for site surveying and inspections, providing real-time data and enhancing safety. In logistics, drones streamline delivery services and inventory management, offering innovative solutions to traditional challenges and significantly improving operational efficiency.
CNC Machines
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are sophisticated automated tools essential for precision machining operations. Governed by computer programs, these machines deliver high accuracy and speed. CNC machines encompass a variety of tools, including milling machines, lathes, and routers. They are integral to industries such as manufacturing, woodworking, and metal fabrication, where they perform critical tasks such as cutting, shaping, and drilling materials with exceptional precision and efficiency.
The diverse range of automation equipment, each tailored to specific applications and industries, offers unique capabilities that have significantly transformed various sectors. Their implementation has revolutionized productivity, enhanced precision, and facilitated the automation of complex tasks, driving efficiency and innovation across numerous fields.
Considerations with Automation Equipment
While automation equipment provides numerous advantages, it also presents potential limitations. A primary concern is job displacement, as advanced machines can take over tasks previously performed by humans, reducing the demand for human labor. Moreover, the implementation and maintenance of automation equipment are costly, and there is an inherent risk of cyber attacks or equipment failure. These factors must be carefully considered when integrating automation solutions into various industries.
Advantages of Automation Equipment
Despite these challenges, automation equipment offers substantial benefits. One of the key advantages is the ability of machines to operate continuously without breaks, significantly increasing output and reducing cycle times, thereby boosting productivity and achieving notable cost savings. Assembly machinery also excels in performing tasks at a much faster rate than human workers, which is crucial in logistics and warehousing.
Furthermore, automation enhances safety in hazardous environments by taking over dangerous tasks. For instance, robots can handle toxic chemicals or operate in high-temperature settings, thereby minimizing the risk of injury to human workers. Automation also ensures high consistency in production, reducing defects and improving product quality. Additionally, by replacing human labor, automation can substantially lower labor costs, a benefit particularly relevant in labor-intensive industries like manufacturing.
Sustainability and Positive Environmental Impact
Automation equipment holds significant potential for enhancing sustainability and positively impacting the environment. A crucial aspect is energy efficiency; advanced robotic systems and optimized machinery are designed to operate with high energy efficiency, thereby reducing energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. Automation also allows for better control and optimization of processes, which minimizes waste and enhances resource utilization. For example, automated systems can precisely measure and dispense materials, thereby reducing material waste and environmental impact.
Moreover, automation facilitates predictive maintenance, allowing for proactive servicing of equipment and reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns that can result in waste or energy inefficiencies. By optimizing production processes and minimizing waste, automation equipment plays a vital role in promoting sustainable practices, helping industries transition towards more environmentally friendly operations.
Adapting to Your Workforce to Automation
The rise of automation equipment necessitates a focus on skills and workforce development to adapt to the changing job landscape. As automation technology advances, the demand for new skill sets and expertise grows. It is crucial to invest in upskilling and reskilling programs to equip the workforce with the necessary knowledge to work alongside automation equipment. This includes developing skills in areas such as robotics, data analytics, programming, and the maintenance of automated systems.
Educational institutions, training organizations, and industry collaborations play a pivotal role in providing relevant training programs and courses. Additionally, fostering a culture of lifelong learning and continuous skill development is vital to ensure the workforce remains adaptable and resilient in the face of technological advancements. Collaboration between industries, governments, and educational institutions is essential to identify emerging skill requirements, design effective training programs, and bridge the skills gap. By prioritizing skills and workforce development, organizations can unlock the full potential of automation equipment while empowering individuals to thrive in the evolving job market.
Applications of Automation Equipment
Automation equipment is widely used in manufacturing to increase production speed and efficiency, reduce defects, and improve product quality. Automation equipment is used in logistics and warehousing to increase the speed and accuracy of order fulfillment, reduce errors, and optimize inventory management.
Automation equipment is used in agriculture to improve crop yields, reduce labor costs, and improve the efficiency of farming operations, while healthare providers use it to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. For example, robotic surgery is increasingly being used to perform minimally invasive surgeries, reducing the risk of complications and reducing recovery time.
In the construction assembly, automation helps to increase productivity and efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve safety. For example, drones can be used to survey construction sites and identify potential hazards.
The Future of Automation Equipment
The future of automation equipment will be shaped by several key trends and developments. Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are expected to significantly enhance automation capabilities, enabling machines to learn, adapt, and make intelligent decisions. This progress could result in more sophisticated and autonomous systems capable of handling complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
The integration of automation equipment across various industries is also anticipated to expand, reaching sectors that have traditionally been less automated. This expansion will likely include fields such as healthcare, agriculture, and construction, where automation technologies can improve efficiency, quality, and safety. The adoption of automation in these areas will drive innovation and operational improvements, transforming how these industries function.
Ethical considerations, including workforce displacement and human-machine collaboration, will remain crucial topics of discussion as automation continues to evolve. Balancing the benefits of automation with the well-being and future employment prospects of workers will require thoughtful policies, educational initiatives, and social support systems. Ensuring that the workforce is prepared for these changes through upskilling and reskilling programs will be essential.
Sustainability and environmental impact will play a vital role in the future development of automation. Emphasizing energy efficiency, waste reduction, and responsible manufacturing practices, automation technologies have the potential to contribute to a greener and more sustainable industrial landscape. By addressing these various dimensions, the future of automation equipment holds great potential for driving innovation, improving productivity, and making a positive societal impact.
Choosing Appropriate Automation Equipment
Choosing the right automation equipment for specific needs requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key steps and considerations to help guide the selection process.
1. Identify Automation Goals: Start by clearly defining the specific goals and objectives you aim to achieve through automation. Determine the tasks or processes that need automation and the desired outcomes, such as increased productivity, cost reduction, or improved quality.
2. Assess Requirements: Conduct a thorough analysis of your operational requirements. Consider factors such as task complexity, production volume, available space, safety considerations, and regulatory requirements. This assessment will help identify the specific capabilities and features needed.
3. Conduct a Feasibility Study: Evaluate the feasibility of automation by analyzing costs, benefits, and potential return on investment (ROI). Consider upfront costs of equipment acquisition, installation, and integration, as well as ongoing maintenance, training, and operational costs. Assess projected benefits like increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, improved safety, and potential revenue growth.
4. Research Available Technologies: Research different automation technologies and equipment available in the market. Consider functionalities, performance capabilities, compatibility with existing systems, and reliability. Consult industry publications, attend trade shows or conferences, and seek input from industry experts to gather insights and make informed decisions.
5. Seek Vendor Support: Engage with reputable vendors or integrators who specialize in your industry. Discuss your specific needs and objectives with them, and seek their expertise in recommending suitable equipment solutions. Vendors can provide valuable insights, conduct on-site evaluations, and help design a customized automation solution that aligns with your requirements.
6. Evaluate Scalability and Flexibility: Consider the equipment’s future scalability and flexibility. Assess whether the equipment can accommodate potential growth in production volumes or changes in processes. Look for modular and adaptable systems that can be easily reconfigured or expanded to meet evolving needs.
7. Test and Validate: Before finalizing the purchase, if possible, conduct pilot tests or trials with the selected machinery. This allows you to assess its performance in a real-world environment and validate its suitability for your specific needs. During the trial phase, gather feedback from operators and stakeholders to ensure the equipment meets expectations.
8. Training and Support: Consider the availability of training and technical support from the equipment manufacturer or supplier. Adequate training for operators and maintenance personnel is crucial to maximize the benefits and optimize the performance of the automation equipment. Ensure that the vendor provides reliable after-sales support, including prompt maintenance and troubleshooting services.
By following these steps and considering the specific requirements and goals, you can make a well-informed decision when choosing automation equipment that best suits your organization’s needs and maximizes the potential benefits of automation.
Choosing the Correct Automation Equipment Supplier
When choosing automation equipment, it is beneficial to compare multiple suppliers using our comprehensive directory. Our directory of automation equipment suppliers features detailed business profiles that highlight each supplier’s areas of expertise and capabilities. Each profile includes a contact form, allowing you to easily communicate with suppliers for more information or to request a quote.
Utilize our proprietary website previewer to quickly gain insights into each company’s specializations by reviewing their websites. This tool streamlines the process of identifying the most suitable suppliers based on your specific needs.
Additionally, our simplified RFQ (Request for Quote) form allows you to contact multiple suppliers simultaneously, providing a consistent basis for comparison. By leveraging these resources, you can make well-informed decisions and select the optimal automation equipment supplier to meet your organization’s requirements.




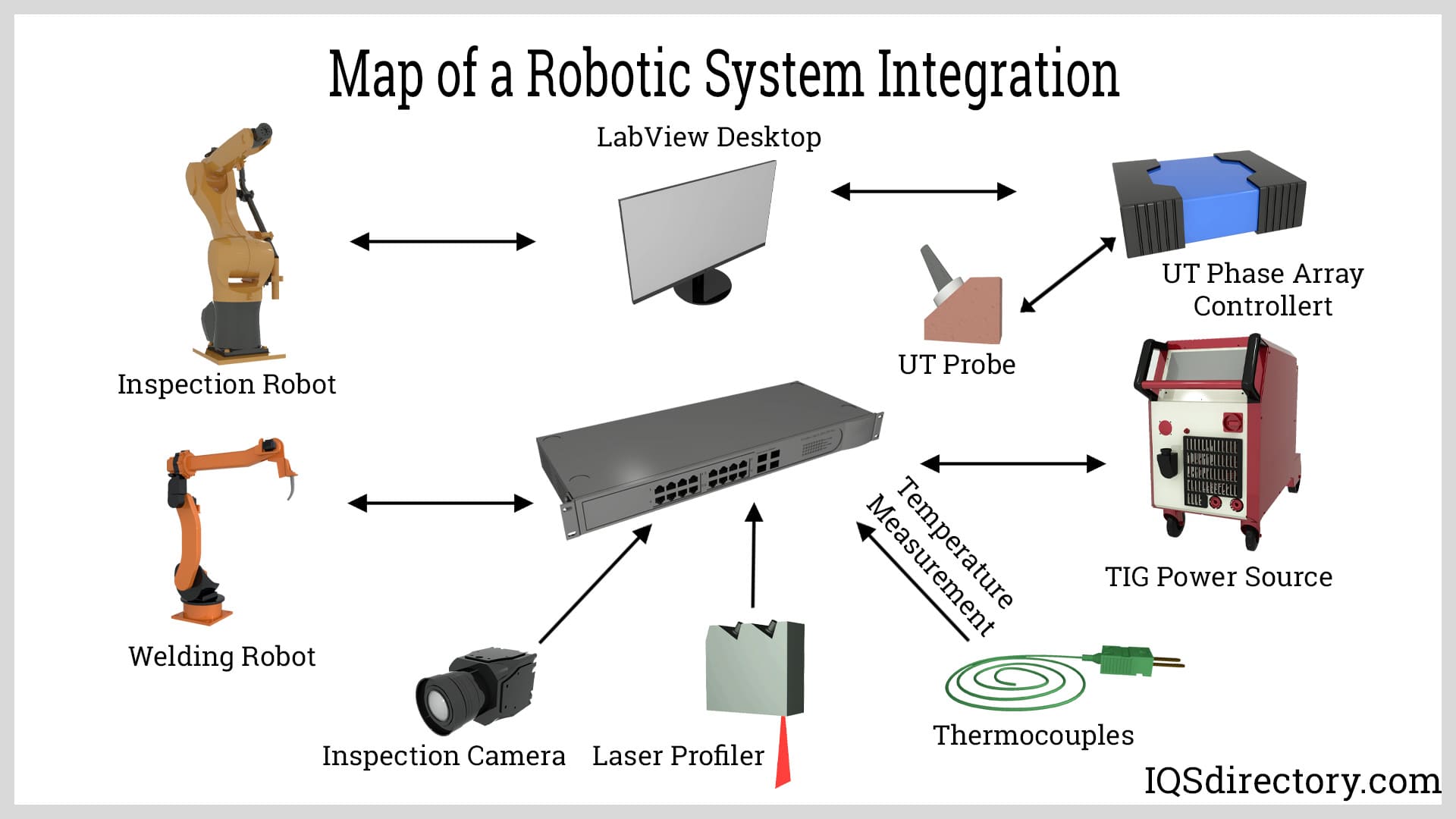


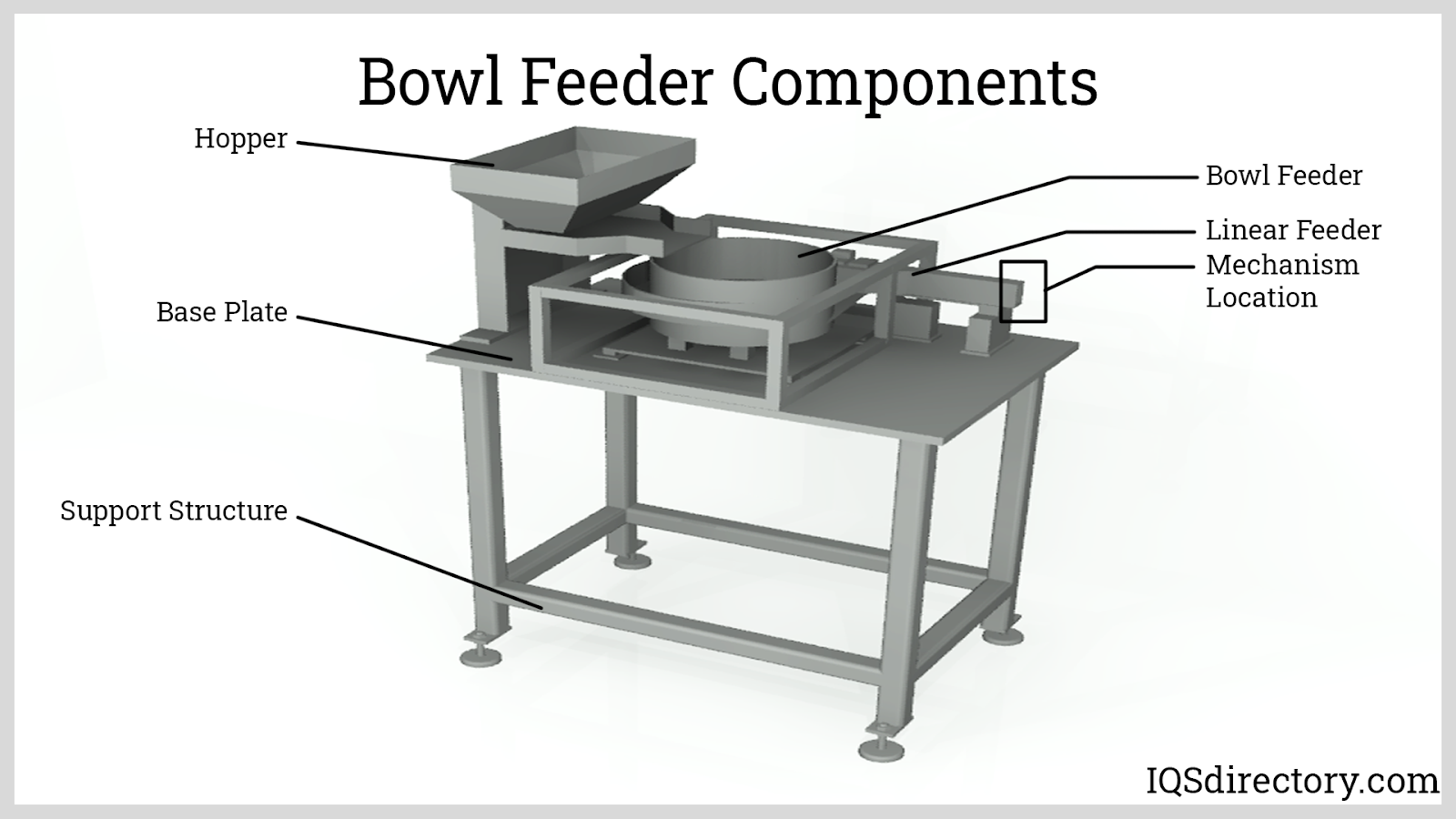
 AGVs
AGVs Casters
Casters Cranes
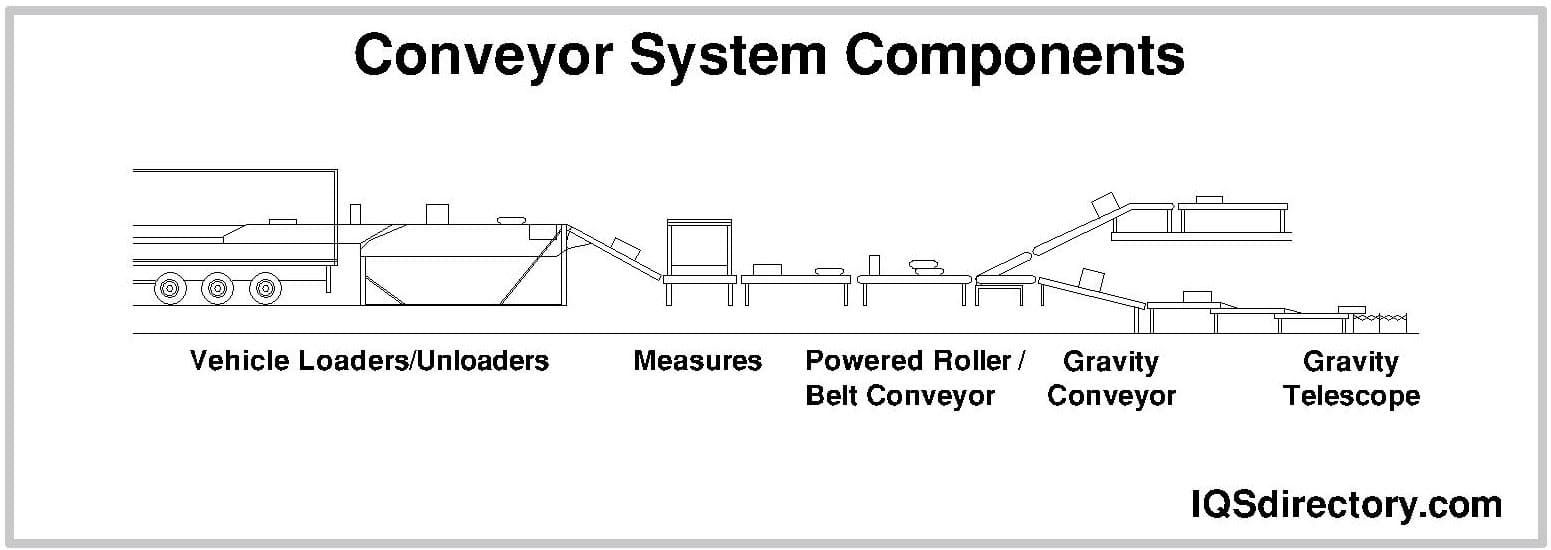
Cranes Conveyors
Conveyors Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists Forklifts
Forklifts Hydraulic Lifts
Hydraulic Lifts Platform Lifts
Platform Lifts Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services